quantitative sampling|types of sampling in quantitative : private label The quantitative research sampling method is the process of selecting representable units from a large population. Quantitative research refers to the analysis wherein mathematical, statistical, or computational method is used for studying the measurable or quantifiable dataset. Resultado da Follow these steps to run the system file checker then reinstall the Epic Games Launcher: Close the Epic Games launcher by right-clicking the system tray icon in the bottom right corner and then clicking Exit. Click Start. Type "cmd", right-click Command Prompt, and then click Run as .
{plog:ftitle_list}
16 de nov. de 2021 · 36氪专访 | 前一加高管、Nothing创始人裴宇:做一款“反无聊”的产品. 融资7000万美元,裴宇想做一个不编故事的品牌。. 迄今为止,裴宇身上最深刻 .
Quantitative researchers are often interested in being able to make generalizations about groups larger than their study samples. While there are certainly instances when quantitative researchers rely on nonprobability samples (e.g., when doing exploratory or evaluation research), quantitative researchers tend to rely on probability sampling techniques. When to use systematic sampling. Systematic sampling is a method that imitates many of the randomization benefits of simple random sampling, but is slightly easier to conduct.. You can use systematic sampling with a list of the entire population, like you would in simple random sampling.However, unlike with simple random sampling, you can also use this . Sampling methods in psychology refer to strategies used to select a subset of individuals (a sample) from a larger population, to study and draw inferences about the entire population. Common methods include .Sampling Designs: There are two broad classes of sampling in quantitative research: Probability and nonprobability sampling. Probability sampling: As the name implies, probability sampling means that each eligible individual has a random chance (same probability) of being selected to participate in the study.
The quantitative research sampling method is the process of selecting representable units from a large population. Quantitative research refers to the analysis wherein mathematical, statistical, or computational method is used for studying the measurable or quantifiable dataset. Quantitative research methods. You can use quantitative research methods for descriptive, correlational or experimental research. In descriptive research, you simply seek an overall summary of your study variables.; In correlational research, you investigate relationships between your study variables.; In experimental research, you systematically examine whether .
Availability sampling is appropriate for student and smaller-scale projects, but it comes with significant limitations. The purpose of sampling in quantitative research is to generalize from a small sample to a larger population. Because availability sampling does not use a random process to select participants, the researcher cannot be sure . Broadly speaking, in quantitative research, two types of samples are used. The first, and most common, is the representative sample. It is important in most research that the sample be . Other well-known random sampling methods are the stratified sample, the cluster sample, and the systematic sample. To choose a stratified sample, divide the population into groups called strata and then take a proportionate number from each stratum. For example, you could stratify (group) your college population by department and then choose a .
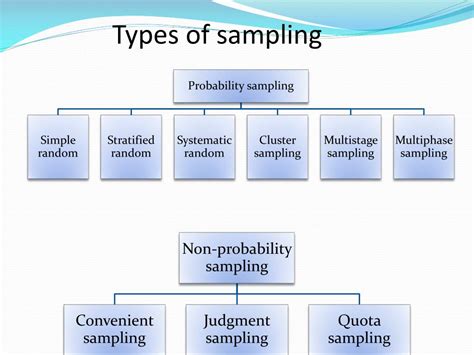
There are two main quantitative sampling techniques: Probability sampling; Non-probability sampling; In a probability sample, every member of the population of interest is equally likely to be chosen to become part of the sample.For example, to recruit a representative sample of members of a social support group, a researcher might randomly select 10% of all listed .15 Sampling Techniques for Quantitative Research 225. Probability Sampling . From its name, probability sampling is applied when elements in the population have an acknowledged equal probability to be selected as subjects. Hence, samples in probability sampling design, compared to non-probability sampling, are a better .
Quota Sampling: In this method, a predetermined number of participants are selected based on specific criteria, such as age or gender. This method is often used in market research, but may not be representative of the population. . The data collected is quantitative and statistical analyses are used to draw conclusions. Probability sampling: Entails random selection and typically, but not always, requires a list of the entire population.; Non-probability sampling: Does not use random selection but some other process, such as convenience.Usually does not sample from the whole population. Probability sampling is typically more difficult and costly to implement, but, in .Quantitative sampling is a statistical method used to select a subset of individuals from a larger population, allowing researchers to make inferences about the entire group based on the analysis of this smaller sample. This approach is essential in fields such as statistics, data analysis, and data science, where understanding trends and .
Chapter Outline. The sampling process (25 minute read); Sampling approaches for quantitative research (15 minute read); Sample quality (24 minute read); Content warning: examples contain references to addiction to technology, .Math: Pre-K - 8th grade; Pre-K through grade 2 (Khan Kids) Early math review; 2nd grade; 3rd grade; 4th grade; 5th grade; 6th grade; 7th grade; 8th grade; 3rd grade math (Illustrative Math-aligned)Whereas sampling in quantitative research focuses on maximizing the statistical representativeness of a population by a chosen sample, sampling in qualitative research generally focuses on the complete representation of a phenomenon of interest. Because of this core difference in purpose, many sampling considerations differ between qualitative .
Quantitative researchers are often interested in being able to make generalizations about groups larger than their study samples. While there are certainly instances when quantitative researchers rely on nonprobability samples (e.g., when doing exploratory or evaluation research), quantitative researchers tend to rely on probability sampling techniques. Quantitative research serves as the cornerstone of evidence-based decision-making. Its importance cannot be overstated: quantitative methods provide empirical rigor, enabling preachers (academia), practitioners (industry), and policymakers (government; i.e. the 3Ps) to derive actionable insights from data. However, despite its significance, mastering the . Quantitative Research. Quantitative research is a type of research that collects and analyzes numerical data to test hypotheses and answer research questions.This research typically involves a large sample size and uses statistical analysis to make inferences about a population based on the data collected.Sampling is the statistical process of selecting a subset—called a ‘sample’—of a population of interest for the purpose of making observations and statistical inferences about that population. Social science research is generally about inferring patterns of behaviours within specific populations. We cannot study entire populations because of feasibility and cost constraints, .
The quantitative researcher seeks a sample that is representative of the population of interest so that they may properly generalize the results (e.g., if 80 percent of first-gen students in the sample were concerned with costs of college, then we can say there is a strong likelihood that 80 percent of first-gen students nationally are .
What Is Non-Probability Sampling? | Types & Examples. Published on July 20, 2022 by Kassiani Nikolopoulou.Revised on June 22, 2023. Non-probability sampling is a sampling method that uses non-random criteria like the availability, geographical proximity, or expert knowledge of the individuals you want to research in order to answer a research question.10.3 Sampling in quantitative research Learning Objectives. Describe how probability sampling differs from nonprobability sampling; Define generalizability, and describe how it is achieved in probability samples; Identify the various types of probability samples, and describe why a researcher may use one type over another .
Probability sampling is used in quantitative research, so it provides data on the survey topic in terms of numbers. Probability relates to mathematics, hence the name ‘quantitative research’. Subjects are asked questions like: How many boxes of .When undertaking any research study, researchers must choose their sample carefully to minimise bias. This paper highlights why practitioners need to pay attention to issues of sampling when appraising research, and discusses sampling characteristics we should look for in quantitative and qualitative studies. Because of space restrictions, this editorial focuses on .10.3 Sampling in quantitative research Learning Objectives. Describe how probability sampling differs from nonprobability sampling; Define generalizability, and describe how it is achieved in probability samples; Identify the various types of probability samples, and describe why a researcher may use one type over another .
types of sampling in quantitative
Package Vertical Steam Boiler —50L distributor
Cap Torque Tester distributor
webLooking for the best Challenger La Manche bets? Here at OddsDigger you'll find the .
quantitative sampling|types of sampling in quantitative